
截止目前,引用Bioss产品发表的文献共34362篇,总影响因子169875.41分,发表在Nature, Science, Cell以及Immunity等顶刊的文献共125篇,合作单位覆盖了清华、北大、复旦、华盛顿大学、麻省理工学院、东京大学以及纽约大学等上百所国际知名研究机构。
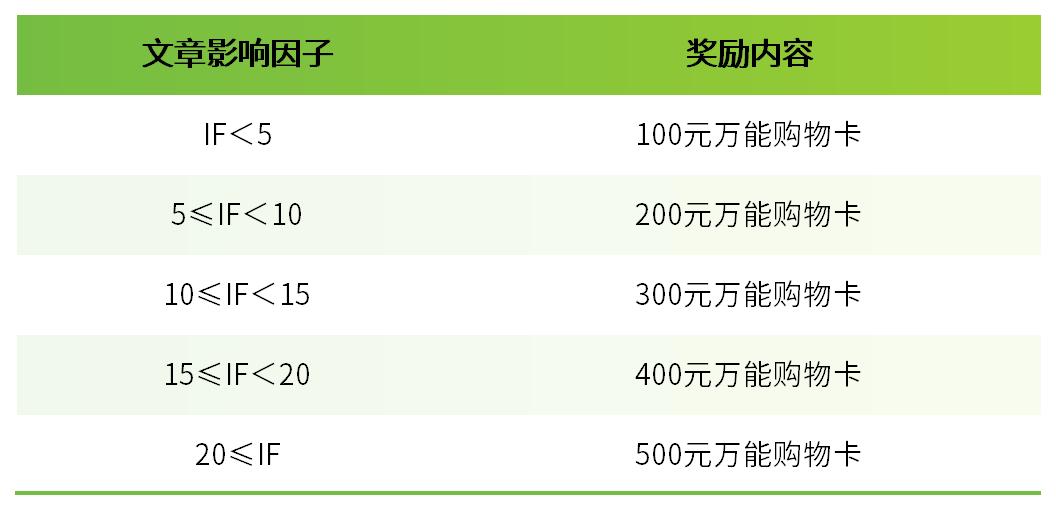
我们每月收集引用Bioss产品发表的文献。若您在当月已发表SCI文章,但未被我公司收集,请致电Bioss,我们将赠予现金鼓励,金额标准请参考“发文章 领奖金”活动页面。
本文主要分享引用Bioss产品发表文章至CELL, Nature Immunology, Cell Metabolism, Advanced Materials, Immunity, Bioactive Materials, ACS Nano等期刊的10篇IF>15的文献摘要,让我们一起欣赏吧。
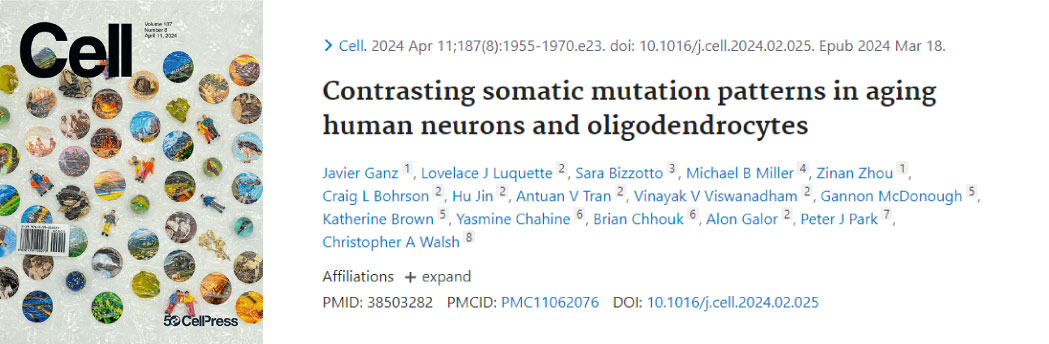
CELL [IF=45.6]
文献引用产品:
bs-5870R | KLK6 Rabbit pAb | Other
bs-1000R | CNPase Rabbit pAb | Other
作者单位:波士顿儿童医院
摘要:Characterizing somatic mutations in the brain is important for disentangling the complex mechanisms of aging, yet little is known about mutational patterns in different brain cell types. Here, we performed whole-genome sequencing (WGS) of 86 single oligodendrocytes, 20 mixed glia, and 56 single neurons from neurotypical individuals spanning 0.4–104 years of age and identified >92,000 somatic single-nucleotide variants (sSNVs) and small insertions/deletions (indels). Although both cell types accumulate somatic mutations linearly with age, oligodendrocytes accumulated sSNVs 81% faster than neurons and indels 28% slower than neurons. Correlation of mutations with single-nucleus RNA profiles and chromatin accessibility from the same brains revealed that oligodendrocyte mutations are enriched in inactive genomic regions and are distributed across the genome similarly to mutations in brain cancers. In contrast, neuronal mutations are enriched in open, transcriptionally active chromatin. These stark differences suggest an assortment of active mutagenic processes in oligodendrocytes and neurons.
Nature Immunology [IF=27.8]

文献引用产品:
bs-3576R-APC-Cy7 | HBEGF Rabbit pAb, APC-Cy7 conjugated | Flow cytometry
作者单位:亚历山大大学
Cell Metabolism [IF=27.7]

文献引用产品:
C0103 | PBS (1×, powder, 2L) | Other
作者单位:武汉大学中南医院
摘要:Bacteria-based metabolic therapy has been acknowledged as a promising strategy for tumor treatment. However, the insufficient efficiency of wild-type bacteria severely restricts their therapeutic efficacy. Here, we elaborately develop an ʟ-cyst(e)ine-addicted bacteria-nanodrug biohybrid for metabolic therapy through a dual-selection directed evolution strategy. Our evolved strain exhibits a 36-fold increase in ʟ-cystine uptake and a 23-fold improvement in total activity of cysteine desulfhydrases compared with the wild-type strain. By conjugating with DMXAA-loaded liposomes, the engineered bacteria-nanodrug biohybrid not only prevents the influx of nutrients into the tumor by blocking neovasculature but also achieves efficient and durable CySS catabolism locally. The unavailable of Cys species disrupts redox homeostasis and strikingly increases intracellular ROS level, achieving favorable therapeutic outcomes in multiple tumor models. Our study not only highlights the promise of directed evolution strategy in enhancing the stability and efficiency of bacteria-based living biocatalyst but also provides new opportunities for antitumor metabolic therapy.
Advanced Materials [IF=27.4]

文献引用产品:
BA00208 | Cell Counting Kit-8 | Other
摘要:Tailored photophysical properties and chemical activity is the ultimate pursuit of functional dyes for in vivo biomedical theranostics. In this work, the independent regulation of the absorption and fluorescence emission wavelengths of heptamethine cyanines is reported. These dyes retain near-infrared fluorescence emission (except a nitro-modified dye) while feature variable absorption wavelengths ranging from 590 to 860 nm. This enables to obtain customized functional dyes that meet the excitation and fluorescence wavelength requirements defined by the optical properties of tissues for in vivo biomedical applications. Typically, a nitro-modified photothermal active derivative Cy-Mu-7-9 is used, which features strong absorption at 810 nm in PBS, a wavelength that balanced the tissue penetration depth and non-specific photothermal effect, to realize non-destructive inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) therapy via photothermal induced up-regulation of heat shock protein 70 in the intestinal epithelial cells. The corresponding amino-modified dye Cy-Mu-7-9-NH2, which can be formed in health enteric cavity by Cy-Mu-7-9 after oral administration, is a fluorescence compound with the emission of 800 nm in PBS. Based on the IBD sensitive transformation of Cy-Mu-7-9 and Cy-Mu-7-9-NH2, in vivo IBD theranostic and therapeutic effect evaluation is realized via the synergy of fluorescence imaging and photothermal therapy for the first time.
Immunity [IF=25.5]

文献引用产品:
bs-1927R | PLAUR Rabbit pAb | ICC
摘要:Thrombotic diseases remain the major cause of death and disability worldwide, and the contribution of inflammation is increasingly recognized. Thromboinflammation has been identified as a key pathomechanism, but an unsupervised map of immune-cell states, trajectories, and intercommunication at a single-cell level has been lacking.
Here, we reveal innate leukocyte substates with prominent thrombolytic properties by employing single-cell omics measures on human stroke thrombi. Using in vivo and in vitro thrombosis models, we propose a pro-resolving monocyte-neutrophil axis, combining two properties: (1) NR4A1hi non-classical monocytes acquire a thrombolytic and neutrophil-chemoattractive phenotype, and (2) blood neutrophils are thereby continuously recruited to established thrombi through CXCL8-CXCR1 and CXCR2 and adopt a hypoxia-induced thrombus-resolving urokinase receptor (PLAUR)+ phenotype. This immunothrombolytic axis results in thrombus resolution. Together, with this immune landscape of thrombosis, we provide a valuable resource and introduce the concept of “immunothrombolysis” with broad mechanistic and translational implications at the crossroad of inflammation and thrombosis.
Bioactive Materials [IF=18]

文献引用产品:
bs-0195R | CD31 Rabbit pAb | IF
bs-5884R-PE | Endomucin Rabbit pAb, PE conjugated | IF
作者单位:南方医科大学
摘要:The treatment of refractory bone defects is a major clinical challenge, especially in steroid-associated osteonecrosis (SAON), which is characterized by insufficient osteogenesis and angiogenesis. Herin, a microenvironment responsiveness scaffold composed of poly-L-lactide (PLLA), and manganese dioxide (MnO2) nanoparticles is designed to enhance bone regeneration by scavenging endogenous reactive oxygen species (ROS) and modulating immune microenvironment in situ. A catalase-like catalytic reaction between MnO2 and endogenous hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) generated at the bone defect area, which typically becomes acidic and ROS-rich, triggers on-demand release of oxygen and Mn2+, significantly ameliorating inflammatory response by promoting M2-type polarization of macrophages, reprograming osteoimmune microenvironment conducive to angiogenesis and osteogenesis. Furthermore, the fundamental mechanisms were explored through transcriptome sequencing analysis, revealing that PLLA/MnO2 scaffolds (PMns) promote osteogenic differentiation by upregulating the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway in human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (hBMSCs). Overall, the PMns exhibit superior immunomodulatory, excellent osteogenic-angiogenic properties and promising candidates as bone graft substitutes for therapy clinical refractory bone defects.
ACS Nano [IF=15.8]

文献引用产品:
bs-1712R | Pan Cytokeratin Rabbit pAb | mIHC
作者单位:中山大学

文献引用产品:
bs-1110R | SP7/Osterix Rabbit pAb | IHC
作者单位:华南理工大学
摘要:Aging-related bone degeneration and impaired healing capacity remain significant challenges in regenerative medicine, necessitating innovative, efficient, and targeted strategies to restore bone health. Here, we engineered extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from the serum of pretreated juvenile mice, with the goals of reversing aging, enhancing osteogenic potential, and increasing bioavailability to rejuvenate the aging bone environment. First, we established bone healing models representing different phases of healing to identify the EV type with the highest potential for improving the bone microenvironment in older individuals. Second, we employed DSS6 for bone targeting to enhance the biological effects of the selected EVs in vivo. The engineered EVs effectively targeted bone repair sites and promoted fracture healing more effectively than unmodified EVs in older mice. RNA sequencing revealed that the translocase of outer mitochondrial membrane 7 (Tomm7) is crucial for the underlying mechanism. Silencing Tomm7 significantly diminished the positive regulatory effects of the EVs. Specifically, the engineered EVs may enhance mitochondrial function in aging cells by activating the Tomm7-mediated Pink1/Parkin mitophagy pathway, promoting stemness recovery in aging bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) and reversing the adverse conditions of the aging bone microenvironment. Overall, the developed engineered EVs derived from serum from juvenile mice offer an alternative approach for treating aging bones. The identified underlying biological mechanisms provide a valuable reference for precision treatment of aging bones in the future.
ACS Nano [IF=15.8]

文献引用产品:
作者单位:南方医科大学
摘要:Adoptive T cell therapy (ACT) is an emerging cancer immunotherapy undergoing clinical evaluation, showing significant promise in the treatment of solid tumors. However, the clinical translation of ACT is hindered by its time-, labor-, and financial-consuming procedures, heterogeneity of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), and immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. Herein, we have developed a bionic cytotoxic T lymphocyte-inspiring microscale system (CTLiMS) composed of mesoporous silica dioxide microspheres containing membrane-disrupting boron clusters (BICs) and proapoptotic monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) peptides. The BICs were found to disrupt the integrity of cancer cell membranes and enhance the internalization of MMAE, effectively mimicking the biological functions of perforin and granzymes released by CTLs to destroy cancer cells. As expected, the CTLiMSs demonstrated exceptional in vitro anticancer activity, inducing cancer cell apoptosis and exhibiting strong antiproliferative effects. Notably, CTLiMS treatment was demonstrated to induce immunogenic cell death of cancer cells as a result of Ca2+ and MMAE influx and subsequent production of reactive oxygen species. The animal studies demonstrated that the CTLiMS treatment led to efficient repression of the tumor growth. Furthermore, the CTLiMS administration resulted in favorable antitumor immunotherapeutic effects, as shown by significant inhibition of distant tumors, increased immune cell infiltration, and elevated plasma levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines. This pilot study using CTLiMSs for cancer immunotherapy offers an innovative bionic strategy for the future advancement of adoptive T cell therapy.
ACS Nano [IF=15.8]

文献引用产品:
作者单位:吉林大学第一医院
